LEADING ARTICLE
REVIEWS AND LECTURES
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
THE AIM. To determine clinical value of acute kidney injury (AKI) in the setting of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for mortality along postransplant period.
PATIENTS AND METHODS. Ninety hematopoietic stem cell transplantat (HSCT) recipients (46 males, 44 females) were enrolled in the observational prospective study. Clinical and laboratory data were monitored and assessed 7 days prior to HSCT (week 0), on the posttransplant weeks 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. AKI was diagnosed according to KDIGO (Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes) guidelines. All-cause mortality was registered along 1 year of posttransplant period. AKI associations with death risk were estimated in cumulative survival analysis and Cox multivariate regression models adjusted for other confounders.
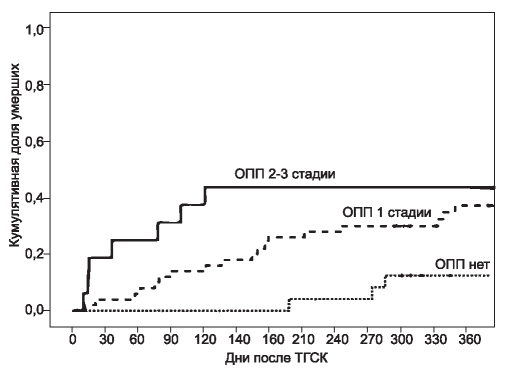
RESULTS. AKI was diagnosed in 67 (74%) out of 90 patients. The majority of patients (84%) suffered from AKI 1 stage (KDIGO). AKI 2+3 stage (KDIGO) was found in 16% of patients. Renal replacement therapy was used in 4 (6%) patients with AKI. Cumulative survival rate following HSCT reached 75%. 28 deaths (31%) were registered within 1 year following HSCT. AKI was associated with lower cumulative survival following HSCT. AKI was independently associated with the risk of death according to multivariate Cox regression analyses adjusted for other confounders.
CONCLUSION. AKI may be considered as a significant clinical predictor of unfavorable allogeneic HSCT outcome, taking into account its independent association with increased risk of posttransplant all-cause mortality.
INTRODUCTION: Renal injury associated with monoclonal gammopathies (MG) is an area of interest of practical onconephrology. Prevalence, spectrum and renal outcome as far as approaches to treatment in this pathological entity, particularly in Russian population, still remain unclear and need refinement. AIM: Analysis of the prevalence, spectrum, treatment approaches and renal outcome in kidney injury associated with monoclonal gammopathies (MG).
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Patients with MG and renal injury proven by kidney biopsies from 01.01.2011 till 01.05.2018 were enrolled into this one-center prospective study (n=119). Cases of MG of undetermined significance and non-amyloid kidney lesions were estimated as MG of renal significance (MGRS). Treatment approaches, haematological and renal responses were analysed. Worsening of kidney function was estimated as eGFR decrease >25 % from initial value or initiation of renal replacement treatment (RRT), improving – as eGFR increase >25 % from the initial value or the discontinuation of RRT. Other cases were determined as stable kidney function. Kidney outcome was determined in RRT initiation or eGFR<15 ml/min/1,73m2 at the end of follow-up. Long-term kidney outcome was estimated by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. The median follow-up period was 12 (2; 27) months.
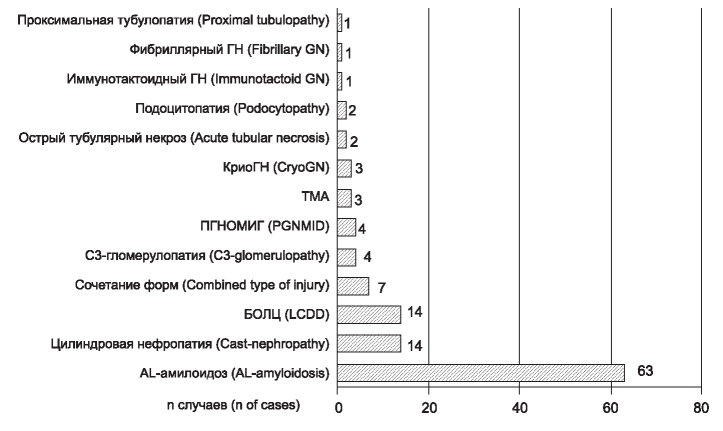
RESULTS. Prevalence of kidney injury associated with MG among all performed kidney biopsies was 7,5 %, MGRS – 0,94 %. Multiple myeloma (MM), AL-amyloidosis and lymphoproliferative disorder (LPD) were diagnosed in 39, 55 and 10 patients, respectively. Prevalence of kidney injury types was the following: Al-amyloidosis (53 %); cast nephropathy (12 %); light chain deposition disease (12 %); C3-glomerulopathy (3 %); proliferative glomerulonephritis (GN) with monoclonal immunoglobulin deposits (3 %); cryoglobulinemic GN (2 %); thrombotic microangiopathy (2 %); podocytopathy (2 %); acute tubular necrosis – 2 %; immunotactoid GN (1 %); fibrillary GN (1 %); proximal tubulopathy (1 %), combination of different types (6 %). Patients mostly were treated with bortezomib and dexamethasone. Autologous stem cell transplantation was performed in 13 patients. Haematological response was achieved in 48,8 %, 45,4 % and 46,7 % of patients with MM, AL-amyloidosis and MGRS, respectively. Worsening of kidney function was registered in 11,1 % of MM and in 37,2 % of AL-amyloidosis; improving or stable kidney function was in 88,9 % and 62,7 % MM and AL-amyloidosis patients, respectively. In MGRS improving (20 %) and stable kidney function (80 %) were detected. Four-years cumulative renal survival in MM, AL-amyloidosis, MGRS and LPD groups was 63 %, 54 %, 80 % and 39 %, respectively, and does not differ between 4 groups.
CONCLUSION: MG-associated kidney disease represented by diverse clinical and morphological patterns is standard problem in routine clinical practice. It is associated with inferior renal outcome and requires a practical implementation of highly-specialized interdisciplinary approach to diagnostics and treatment.
THE OBJECTIVE of the study was to assess the impact of the count of interstitial CD3+, CD68+ and CD20+ cells on long-term prognosis of renal allograft (RA).
PATIENTS AND METHODS. 86 RA recipients with biopsy-proven according to the Banff 2013- 2017 criteria glomerulitis were enrolled in this retrospective study. The patients were subdivided into the following groups: 1) isolated glomerulitis with negative donor-specific antibodies (DSA) at the biopsy (n=53); 2) glomerulitis with positive DSA (n=22); 3) glomerulitis with undetermined DSA (n=11). Quantitative assay of interstitial positive cells was performed after immunohistochemical staining for CD68+, CD3+, CD20+. The Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards regression model were used for the analysis of the relationship between interstitial CD3+, CD68+, CD20+ cells and risk of RA loss.
RESULTS. CD68+ and CD3+ cells prevailed in interstitium in RA glomerulitis. CD20+ infiltrates were found in 60% of cases. CD20+ cells tended to form infiltrates, in 9 cases these infiltrates reached large sizes (≥ 50 CD20+ lymphocytes) and formed nodular structures. There was no difference in the count of interstitial CD3+ and CD68+ cells and in the presence of CD20+ infiltrates between DSA subgroups. Interstitial CD68+ ≥ 5 cells per field of view (FOV) (x400) and CD3+ ≥ 8 cells per FOV (x400), as well as the presence of large CD20+ infiltrates were associated with a lower RA survival (plog-rank < 0,05). Interstitial CD68+ (≥ 5 cells/FOV), CD3 + (≥ 8 cells/FOV) and the presence of large CD20+ interstitial infiltrates were independently associated with the risk of RA loss in the multivariable Cox regression analysis adjusted for DSA, cold and warm ischemia time (p < 0.05). CONCLUSION. Grade of interstitial infiltration by CD68+, CD3+ and CD20+ cells in RA glomerulitis could be independent predictor of RA loss.
THE AIM: to assess the effect of APOE and SLCO1B1 gene polymorphism on the course of myocardial infarction (MI) associated with acute kidney injury (AKI) in hospital and long-term periods.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: 132 patients with МI were examined, which were divided into 2 groups: the first (I) – 68 patients with MI and AKI, the second (II) – 64 people with MI without AKI.
RESULTS: In the distribution of genotypes, polymorphism of Leu28Pro of the APOE gene in the studied groups was revealed that LeuPro was more often inherited in patients of group I – 20,6 %, the average value of total cholesterol (TC) – 6,01±0,3 mmol/l, and low density lipoproteins (LDL) – 3,37±0,21 mmol/l, compared with patients of group II, where the LeuPro genotype – 6, 2 %, TC – 5,03±0,3 mmol/l, LDL – 2,38±0,3 mmol/l, p<0,05. A similar situation was typical for the polymor phism Val174Ala SLCO1B1 gene, where ValAla in patients of group I-26,5 %, in II-12,5 %, p<0.05. In heterozygotes I sample TC-5,59±0,3 mmol/l, and LDL – 3,30±0,14 mmol/l, in group II TC – 5,19±0,29 mmol/l, LDL – 2,75±0,23 mmol / l, p<0,05. The clinical picture of the hospital period in patients with MI and AKI, proceeded with the development of a greater number of complications, which reflected in the high mortality in group I – 16,2 %, in group II – 4,7 %, p<0,05. In the posthospital period, against the background of atorvastatin administration in both study groups, there was a positive trend of decrease in TC and LDL, but it was not possible to achieve the targets. Mortality in the long-term period in group I – 15,4 %, in group II-2,0 %, p<0.05.
CONCLUSIONS: in patients with MI and AKI on the background of a more severe clinical course of the disease, both in hospital and in the long-term period, rare allelic variants of the genes APOE and SLCO1B1 were more often determined, which negatively affected the lipid profile.
THE AIM. Investigation of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) risk factors prevalence in men under 60 years old with myocardial infarction (MI) and renal dysfunction depending on a year season for enhanced prevention and treatment management of aforementioned target population.
PATIENTS AND METHODS. In-patient treatment results analyses of 412 men in total under 60 y.o. with MI for the period of 2000-2015 indicated that within primary 48 hours from the MI onset 61 patients were having 30-59 mL/min/1,73 m2 estimated glomerular filtration rate (CKD-EPI 2009, modification 2011) and 351 patients were having more than 60 mL/min/1,73 m2 respectively. Collection of supplemental information about MI promotive conditions and disease triggers was done with their manifestation rate comparison in groups of patients with renal dysfunction (RD) and normal CKDEPI. Seasonal differences evaluation was performed with separation of events by climatic time intervals based on mean daily air temperature changes in St. Petersburg, Russia.
RESULTS. RD was observed in 14.8% of the examined cases. The frequency of its detection prevailed in the spring and winter (22% each) seasons. Arterial hypertension (AH), mild obesity, hypertensive crisis events, frequent colds occurrences were noted to be detected more frequently in patients with the RD. Moderate obesity along with Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) manifestations depending from a year season were noted less frequently. In first hours from a MI onset, RD patients demonstrated expressed dyslipidemia evidences due to hypertriglyceridemia and elevated levels of very low density lipoproteins (VLDL).
CONCLUSIONS. AH was noted to be the main cause of DP in men under 60 years old in their initial hours from the IM onset. Its presence in combination with frequent colds predisposition, regardless of diabetes and obesity presence in spring and winter attributes RD development risk in MI acute period. Dyslipidemia is indicative for this type of patients, and that brings the need to assess triglyceride and VLDL blood levels.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION
INTRODUCTION. It is suggested that fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) and its co-receptor Klotho are probably associated
with changes in calcium metabolism in chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to ability to regulate intracellular Ca transport by
modulating the cationic channels TRPV5 and TRPV6.
THE AIM is to investigate the association between Klotho, FGF23 and renal excretion of Ca in the initial stages of experimental CKD.
MATERIAL AND METHODS. The experimental models of chronic kidney injury were resection of the renal tissue in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Serum concentrations of intact FGF23 and PTH were determined by ELISA, renal Klotho protein expression by IHC. The indices of Ca excretion were calculated.
RESULTS. Serum creatinine concentration, creatinine clearance and the severity of interstitial fibrosis in experimental models corresponded to the initial stages of chronic kidney disease. UCa24 and FECa were higher, Klotho protein expression was lower in groups with more severe renal dysfunction, without significant differences in FGF23 and PTH levels. Multiple regression analysis showed that FECa and UCa24 were not associated with FGF23, Klotho, and PTH.
CONCLUSION. Renal excretion of Ca in initial stages of experimental kidney damage is not associated with Klotho and FGF23 levels.
PROGRAM ON CONTINUOUS POSTGRADUATE EDUCATION ON NEPHROLOGY
HIV-positive individuals are at increased risk for kidney disease, including HIV-associated nephropathy, noncollapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, immune-complex kidney disease, and comorbid kidney disease, as well as kidney injury resulting from prolonged exposure to antiretroviral therapy or from opportunistic infections. Clinical guidelines for kidney disease prevention and treatment in HIV-positive individuals are largely extrapolated from studies in the general population, and do not fully incorporate existing knowledge o f the unique HIV-related pathways and genetic factors that contribute to the risk of kidney disease in this population. We convened an international panel of experts in nephrology, renal pathology, and infectious diseases to define the pathology of kidney disease in the setting of HIV infection; describe the role of genetics in the natural history, diagnosis, and treatment of kidney disease in HIV-positive individuals; characterize the renal risk-benefit of antiretroviral therapy for HIV treatment and prevention; and define best practices for the prevention and management of kidney disease in HIV-positive individuals.
ANNIVERSARIES
INDEXES
ISSN 2541-9439 (Online)