SALUTATORY WORD
REVIEWS AND LECTURES
The Contrast Media Safety Committee (CMSC) of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology (European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR)) updated its 2011 guidelines for the prevention of post-contrast acute kidney injury (PC-AKI). The recommendations are based on literature review data. The updated guidelines will be presented in two parts: Part 1 are discussed clarification of terminology (in particular differences between PC-AKI and contrast-induced nephropathy), the best ways to estimate glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). There were refined risk factors of PC-AKI, including by intravenous and intra-arterial routes of administration of the contrast agent. The key points of the updated recommendations are: 1. PC-AKI is the preferred term to characterize the impairment of renal function after the administration of a contrast agent; 2. PC-AKI has many causes for development; 3.Risk of development of AKI with intravascular injection of a contrast agent, overestimated; 4. Important risk factors for PC-AKI are chronic kidney disease and dehydration.
Vitamin D deficiency is among the conditions that are currently causing increased interest due to the high prevalence in almost all regions of the world and are characterized by extremely adverse consequences for the health and quality of life of patients. Large-scale studies conducted in recent years have demonstrated a high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in various age groups, various diseases and various geographical regions. The active study of extraossaos (non-calcemic) effects of vitamin D made it possible to evaluate its diverse effects, including immunotropic, effects on the heart and skeletal muscles, the direct effect on the β-cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans, adipocytes, the synthesis of hormones and a number of biologically active substances. Currently, enough information has been accumulated on the effect of vitamin D on the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). In patients with CKD, decreased calcitriol production in the proximal tubule of the kidney is associated with the risk of nephrosclerosis and arterial hypertension. The timely detection of vitamin D deficiency is difficult due to the diversity of clinical manifestations, erased, low-symptom, and often atypical course in various diseases. Screening for vitamin D deficiency in genetic risk groups is recognized as one of the primary prevention methods for many chronic noncommunicable diseases, including autoimmune, renal, and oncological diseases.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
The aim: to study the relationship of autophagy activity, apoptosis and intracellular protein degradation with body composition in patients with chronic kidney disease 5d.
Patients and methods. A cohort prospective study was performed on 106 adult patients with chronic kidney disease 5d receiving programmed hemodialysis treatment. The data of clinical and anamnestic
Original articles Clinical investigations (complaints, anamnesis), physical (objective examination) and laboratory (Beclin-1, 20S proteasome, Bcl-2) examinations were studied. The latter is performed on the “RADIM analyzer” (USA) using the ELISA kits (“Cloud-Clone Corp.”, USA).
Results. In 80 patients, the activity of autophagy (Beclin-1), intracellular protein degradation (20S-proteasome) and apoptosis (Bcl-2), which was classified into clusters, was determined: “high activity” Beclin-1 was 2.4 ± 0.4 ng / ml, "low activity" - 1.4 ± 0.2 ng / ml; similar clusters of 20S-proteasomes - 62.0 ± 7.1 ng / ml and 31.9 ± 6.7 ng / ml; Bcl-2 - 4.2 ± 0.6 ng / ml and 1.8 ± 0.5 ng / ml, respectively (p <0.05). The low activity of Beclin-1 and the high 20S proteasome and Bcl-2 corresponded to a low lean mass. The low activity of Beclin-1 corresponded to a low indicator of total water. The low activity of the 20S proteasome and Bcl-2 corresponded to a high total water content. The low activity of Beclin-1 corresponded to a low total fluid volume. The low activity of the 20S proteasome and Bcl-2 corresponded to a high total fluid volume. The increase in fluid volume was due to both intracellular and extracellular water.
Conclusion. Patients with CKD 5d stages are characterized by a decrease in the activity of autophagy, apoptosis and intracellular protein degradation due to intracellular energy deficiency. The influence of autophagy, apoptosis and protein degradation on the indicators of lean mass, total water and total fluid volume is accompanied by the simultaneous activation of one process and inhibition of another.
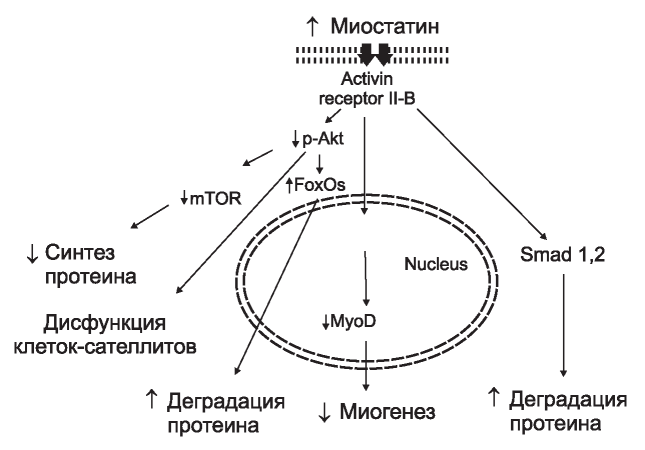
The aim: to assess the effect of myostatin (MSTN) on the development of clinical and laboratory manifestations of protein metabolism disorders in patients receiving hemodialysis.
Patients and methods: 80 patients with CKD 5D stage (47 males and 33 females) were treated with programmed hemodialysis. All patients underwent a thorough collection of clinical and anamnesis data, laboratory monitoring with the determination of the level of MSTN in the blood by enzyme immunoassay, dynamometric and bioelectrical impedance research. Statistical analysis was performed using “STATISTICA 10.0” (“StatSoft Inc.”, USA) and “Microsoft Office Excel 2010” (“Microsoft Corp.”, USA).
Results: the regression analysis did not reveal a statistically significant association of MSTN levels with clinical indicators of protein-energy insufficiency (PED), albumin, β2-microglobulin, CRP, and blood ferritin. Neither the use of various drugs (with the exception of ketoamino acids), nor the presence of a concomitant pathology in history, did not change the level of MSTN. At the same time, the dependence of the local increase in the thickness of the skin folds with the test marker was revealed, the increase in which is associated with a progressive decrease in muscle strength.
Conclusion: as a result of the study, the relationship between the serum concentration of myostatin and the clinical and laboratory manifestations of PEM was evaluated. The obtained data characterize the contribution of MSTN to the process of muscle protein degradation, which may become a target for targeted therapeutic effects and requires further study.
The aim: to evaluate the renal function in conjunction with the rigidity of the magistral arteries and the vascular age in patients with arterial hypertension (AH) and diabetes mellitus (DM) type 2.
Patients and methods. 280 hypertensive patients 45-65 years old with unachieved target blood pressure (BP) values were divided into two groups comparable by clinical and demographic characteristics: the 1 (main) group included patients with AH and DM type 2, the 2 (control) group included patients with AH without DM type 2. Clinical examination, assessment of the renal function, rigidity of the magistral arteries and vascular age were conducted.
Results. A significant increase in the level of albuminuria (AU) - 223.4 [91.4; 329.2] vs 26.4 [8.88; 65.0] mg/g, and β2-microglobulins in the urine (0.445 [0.300; 0.612] vs 0.228 [0.114; 0.398] mg/l) and a statistically significant decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in patients of group 1 compared with patients of group 2 (63.0 [55.0; 73.0] vs 72 [61.5; 88] ml/min/1.73 m2) were noted. The pulse wave velocity through the vessels of the elastic and muscular types (PWVe. and PWVm.) were higher in patients with AH and DM type 2 than in patients with AH without comorbid pathology (10.2 [9.0; 12.2] vs 9,0 [8.0; 10.7] m/s and 9.1 [7.9; 10.4] vs 8.4 [7.5; 9.6] m/s, respectively, p<0.05 ). The vascular age was significantly higher in the main group than in the control group (69.0 [64.0; 73.0] vs 64.0 [57.0; 71.0] years, respectively). We revealed highly reliable relationship between renal function, the rigidity of large vessels and vascular age.
Conclusion. The study showed a significant progressive deterioration of the renal function and the elasticity of the vascular wall of the magistral arteries, the growth of the vascular age, an increase in the 5-year risk of cardiovascular complications in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes compared with patients with “isolated” AH with comparable office blood pressure in the studied groups.
Currently, girls with urinary tract infection (UTI) have a high incidence of chronic vulvovaginitis.
The aim: to study the state of the vaginal biotope in girls of preschool age with urinary tract infections.
Patients and methods. A prospective controlled randomized study was conducted in 88 girls aged 3-6 years with UTI, of whom 1 group (n = 36) with rare UTI (no more than 3 times a year); group 2 (n = 32) - with frequent recurrences of UTI (more than 3 times a year). The control group consisted of 20 girls of similar age without a UTI in the anamnesis. Vaginal microbiocenosis was assessed by bacterioscopic, bacteriologically and by using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Results. In patients with frequent recurrences of UTI, chronic vulvovaginitis was detected significantly more often than in rare relapses. In patients with frequent UTI with a vaginal smear microscopy, in all cases there was a leukocyte reaction (more than 15 leukocytes in the field of view). Leukocytes had a neutrophilic character. When crops were significantly more frequent than in the control and 1st group, the presence of Esherichia coli was noted. According to the results of quantitative PCR, a large number of facultative aerobes were noted with abundant growth (> 105 CFU / ml). Interferon effectiveness was pathogenetically justified in combined urogenital infections.
Conclusion. UTIs make a significant contribution to the development of dysbiosis of the vaginal biotope in preschool girls in the form of the prevalence of gram-negative aerobic microflora. Correction of chronic vulvovaginitis in girls with UTI should be complex, improvement is achieved using interferon.
Background. Currently, adolescent girls with recurrent urinary tract infection (UTI) have a high incidence of reproductive disorders. THE AIM: to study the features of the hormonal profile of adolescent girls with urinary tract infections, depending on the frequency of relapses.
Patients and methods. A prospective controlled randomized study was conducted in 156 adolescent girls aged 15-17 years and 11 months 29 days, including 1 group (n=41) - patients with acute urinary tract infection; 2 group (n=43) - with rare relapses of chronic urinary tract infection; 3 group (n=42) - with frequent recurrence of urinary tract infection; 4 group (n=30) - healthy girls of similar age without urinary tract infection. The concentrations of gonadotropic (luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, prolactin) and steroid (estradiol, testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, cortisol) hormones were studied. All studies were performed on the 5-7 day of the menstrual cycle, progesterone - on the 22-24 day by enzyme immunoassay.
Results. Patients of the 3rd group with often recurrent UTI, compared with patients of groups 1 and 2, showed a significant increase in the levels of luteinizing hormone, testosterone, cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, with a decrease in estradiol concentrations. Progesterone levels determined on days 22-24 from the onset of menstruation in patients with frequent recurrences of UTI were significantly lower than in patients of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and control groups. In patients with acute UTI in the presence of the ovulatory cycle, the hormonal status was similar with the control group. At the same time, in terms of anovulation, an increase in luteinizing hormone, cortisol, was observed against the background of a tendency to a decrease in follicle-stimulating hormone. In patients of group 2 with rare recurrences of UTI in the presence of the ovulatory cycle, the hormonal status was similar with the control group (p> 0.1), in anovulation conditions, in comparison with the control, there was a significant increase in cortisol and luteinizing hormone. In 90.5% of patients of the 3rd group with frequent recurrences of UTI there was no ovulatory cycles.
Conclusion. In adolescent girls with frequent relapses of UTI, there are marked disorders of hormonal status in the form of hypoprolactinemia, increase the level of cortisol and testosterone. The basis of the development of reproductive disorders is the formation of chronic anovulation, which requires a pathogenetic correction.
The aim: to evaluate the effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) therapy on the course of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in children with urinary system congenital malformations.
Patients and methods. 119 patients with urinary system congenital malformations aged 3 to 18 years were examined. A control group of 10 clinically healthy children. There were 3 groups: I - 55 children with congenital vesicoureteral reflex, II - 34 children with congenital hydronephrosis, III - 30 children with other forms of urinary systems dysembryogenesis. ACEI therapy "Enap" ("KRKA", Slovenia), held for 6 months (children up to 14 years at a dose of 0.2 mg/kg/24 h in 1 reception, adolescents 5-10 mg/24 h in 1 reception).
Results. were evaluated according to clinical data, according to the daily monitoring of blood pressure (BP), renal function, renin concentration, plasma aldosterone. Renin and aldosterone production was determined in blood plasma (lying down) by enzyme immunoassay. Results. During ACEI treatment in all children there was stabilization of BP, renal function improvement. Patients with hypertension showed a significant decrease in the concentration of renin. ACEI therapy leads to normalization of aldosterone concentration in patients with hypertension and without hypertension.
Conclusion. The analysis of the course of CKD in patients with US CM on the background of ACEI therapy demonstrates the main aspects of the anti-fibrotic action of the pharmacological blockade of the renin-aldosterone ACEI system.
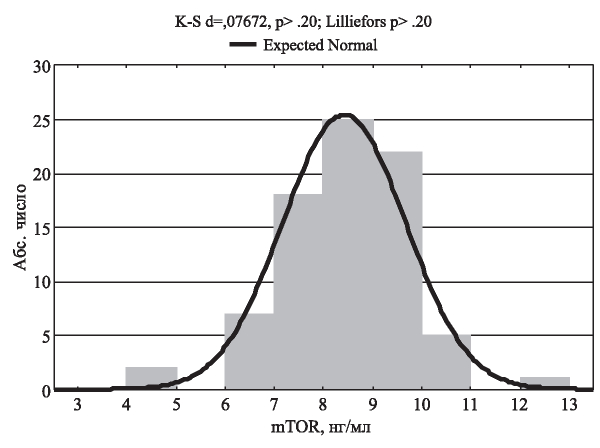
The aim: to assess the prevalence of protein-energy wasting (PEW) and reduction of muscle strength in patients with chronic kidney disease C5D stage (CKD5D), and to determine the role of mTOR in the processes of protein degradation and the development of sarcopenia in the studied group.
Patients and methods: The study included 80 patients with CKD5D (47 men and 33 women) receiving hemodialysis treatment. The average age was 51.7 ± 11.6 years. All patients underwent dynamic dy-namometry, bioimpedancemetry, and determination of the level of mTOR (“ELISA Kit”, USA) in the blood serum using an open enzyme immunoassay.
Results: The prevalence of PEW (according to Bilbrey, Cohen) in the group was 91.5% in men and 87.9 % in women. A decrease in muscle strength was found in 12.8 % of men and in 27.3 % of women. A statistically significant relationship was found between the mTOR level and the “dry weight,” basal metabolism, fluctuation of the dose of iron, average monthly dose of iron. A weak direct correlation between muscle strength and daily caloric intake of food (r = 0.22, p<0.05) was revealed.
Conclusion: Our data were confirm the involvement of mTOR in the activation of catabolic processes in patients with CKD5D and the development of sarcopenia, clinically manifested by a decrease in muscle strength. mTOR can be considered as a promising prognostic molecular marker in assessing the risk of sarcopenia in patients with CKD5D.
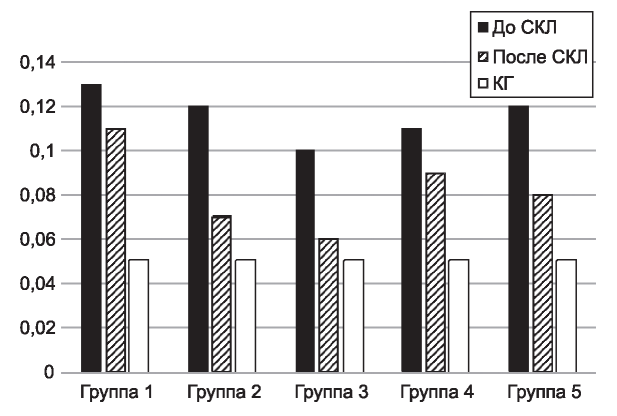
The aim: to study the effect of various integrated spa treatment schemes on the β2-microglobulin (β2MG) dynamics of blood serum and urine in children with various clinical forms of chronic pyelonephritis (CP).
Patients and methods. 254 children with CP, aged 6 to 16 years were included in the study. Secondary CP was diagnosed in 205 (80.71 %) children, primary CP was diagnosed in 49 (19.29 %) children. Patients were randomized into 5 groups: 1 group (n = 48) - comparison group. Spa treatment included a sanatorium-resort regimen, diet 5, physiotherapy, climatotherapy, phytotherapy and balneotherapy. Patients of all subsequent groups, in addition to basic therapy, received peloidotherapy. Children of the 2 group (n = 56) received 6 procedures of galvanopeloidotherapy on the projection area of the; children of 3 group (n = 54) - received 10 procedures of amplipulse peloid therapy on the projection area of the kidneys. Children of the 4 group children (n = 46) received 10 procedures of mud applications on the panty zone. Children of the 5 group 5 (n = 50) received 8 procedures of mud applications on the lumbar projection area. Determined p2-MG in serum and urine using standard sets "DRG int., Inc.", USA.
Results. In patients with secondary CP before treatment, an increase in p2-MG in both biological media was diagnosed, in patients with primary CP, only in urine. On the background of a comprehensive spa treatment, the urine β2-MG concentration in patients with primary CP was statistically significantly reduced in all groups. Normalized - in 2, 3 and 5 groups. Patients of groups 2 and 3 had a significant difference from the result of the comparison group. In patients with secondary CP 3, the β2-MG group in both biological media reached reference values. In group 4, it was normalized in serum and significantly reduced in urine. In groups 1,2 and 5, there was no significant change in the level of urine β2-MG in urine, and in serum there was only in group 5.
Conclusion. For normalization of serum β2-MG and urine in patients with CP it is advisable to conduct peloidotherapy. The area of mud exposure, duration, combination with the preformed physical factor is determined individually, depending on the clinical form of CP.
PRACTICAL NOTES
Thrombotic microangiopathies (TMAs) are induced by several underlying conditions; most are resolved by treating background disease. Eculizumab is a human monoclonal antibody that blocks the final stage of the complement system and effectively treats atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS). In this report, we present a patient with TMA related to sepsis- induced coagulopathy, who was successfully treated with eculizumab.A 44-year-old woman, who had no special medical history or familial history of TMAs, hospitalized for acute kidney injury.Blood tests revealed a decreased platelet count, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), renal dysfunction, hemolysis, and infection. Although the coagulation disorder improved with intensive care, the low platelet count, elevated lactate dehydrogenase levels, and renal dysfunction persisted. Our investigations subsequently excluded thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli-induced HUS. Plasma exchange only improved lactate dehydrogenase levels. We clinically diagnosed this case as atypical HUS and started eculizumab treatment. The patient's platelet count increased, her renal dysfunction improved. We encountered a case of complement-mediated TMA accompanied by DIC, which was successfully treated with eculizumab. Further studies are necessary to support the optimal use of eculizumab for TMA with background diseases.
ISSN 2541-9439 (Online)