REVIEWS AND LECTURES
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
THE AIM: to study the features of the structural and the functional state of the kidneys in relation to the functional state of the endothelium in patients with arterial hypertension (AH) in combination with metabolic disorders.
PATIENTS AND METHODS. The study included 351 patients with AH in the age from 40 to 70 years old with unachieved target values of arterial blood pressure (BP). Patients were divided into four groups, comparable in age, sex, frequency of smoking, duration of AH, the level of office systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP), depending on the presence of concomitant diseases: obesity, MS, type 2 diabetes. Clinical examination with analysis of the body composition was performed, structural and functional parameters of the kidneys, functional state of the endothelium were determined.
RESULTS. The study revealed regular features of changes in the structural and functional parameters of the kidneys in patients with “isolated” AH and in individuals with AH in combination with comorbid pathology in the form of a statistically significant increase of kidney volume, percentage of patients with an uneven contour of the kidneys, impaired structure and changes in echogenicity of the parenchyma, decrease tubular and glomerular functions of the kidneys when AH combines with metabolic disorders. We noted parallelism in structural and functional changes of the when MS components were attached to the AH.
CONCLUSION. The revealed reliable correlation relationships between the structural and functional state of the kidneys and endothelial dysfunction confirm the progression of renal and endothelial damage when MS components are associated with AH.
THE AIM: to study relationship between MCP-1 concentrations with various clinical and morphological manifestations of inflammatory and fibrotic process in renal parenchyma in chronic glomerulonephritis.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: 80 patients with chronic glomerulonephritis were examined. We revealed nephrotic syndrome in 30 patients and nephritic syndrome in 50 patients. Mean age of patients was 35,7±13 years, among them male - 52, female – 28. Average duration of nephritis was 5,0±2,8 years. All patients was performed general examination, estimated creatinine and urea levels of blood serum, calculated glomerular filtration rate (CKD-EPI). Also determined MCP-1 level in blood serum, performed needle nephrobiopsy (optical microscopy, immunofluorescent assay, electron microscopy) with calculation of tubulointerstitial fibrosis activity.
RESULTS. Due to increase of MCP-1 level in blood serum increases fibrosis severity (r = 0,23, p<0,05). Revealed correlation relationship between MCP-1 level and urea of blood initial (before treatment) as well as on treatment and 9 month observation of the patients (r=0,56, p<0,0001, r=0,56, p<0,0001). No statistically significant relationship with creatinine level (r=0,08, p=0,5) or GFR (r=-0,04, p=0,7) was found.
CONCLUSION. Showed relationship between MCP-1 level of blood serum with tubular interstitial fibrosis severity, by that is proved the role of MCP-1-mediated mechanism of tubular interstitial fibrosis progression in chronic glomerulonephritis. Determined no influence of increased MCP-1 levels on tubular interstitial fibrosis and its components occurance which is probably an indication of the prevalence of other MCP-1-mediated mechanisms in formation of tubular interstitial fibrosis, reserving for MCP-1 only the role of tubular interstitial fibrosis progression. Revealing the relationship of MCP-1 with IgA deposits in mesangium and anses capilly loops can probably prove the role of MCP-1 in IgA-nephropathy development, but this study doesn’t show which role is it.
THE AIM: to clarify the possible pathogenic links between the markers of bone mineral metabolism – OPG and RANKL – with markers of cardiovascular diseases characterizing the state of the myocardium and the vascular wall of the aorta in patients undergoing renal replacement therapy.
PATIENTS AND METHODS. 105 patients with C5D CKD were examined: 47 men and 58 women aged 23 to 69 years (mean age -53 ± 2.5 years). The levels of calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone (PTH), osteoprotegerin morphogenetic proteins (OPG) and RANKL (ligand of the receptor activator for the treatment of Kappa B), cardiospecific protein troponin I have been determined. With the help of echocardiography «ALOKA 4000» examined the morphofunctional features of the left ventricle (LV) and aorta. The LV myocardial mass index (LVMI), peak systolic velocity in the aortic arch (Vps) were determined.
RESULTS. Changes in bone mineral metabolism, including an increase in OPG and an increase in the ratio of OPG / RANKL in patients with terminal renal failure, were closely related to an increase in LVMI, a decrease in the LV ejection fraction (LVEF), and an increase in the level of troponin I.
CONCLUSION. In patients with end-stage renal failure, changes in bone mineral metabolism, including a significant increase in the level of OPG and the ratio of OPG / RANKL, are revealed, which indicates a high risk of remodeling processes in the cardiovascular system (CVS), which should be taken into account when choosing cardioprotective therapy.
THE AIM: to research the effect of serum concentrations of resistin on various clinical and morphological manifestations of chronic glomerulonephritis.
PATIENTS AND METHODS. The study included 80 patients with chronic glomerulonephritis, of which 45 patients had IgA-nephropathy, 17 – focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, 10 – membranous nephropathy, 6 – minimal change disease, 1 – IgM-nephropathy, 1 – type I membrane-proliferative glomerulonephritis. 30 patients had a nephrotic variant of nephritis, 50 patients had a nephritic variant (hypertonic). The average age of the patients was 36.2 ± 1.27 years, of which 51 were males and 29 females. The level of the creatinine of blood, urea was estimated, glomerular filtration rate was (CKD-EPI) was calculated. The level of resistin in serum was also determined. All patients underwent needle nephrobiopsy (optical microscopy, immunofluorescent assay, electron microscopy).
RESULTS. Statistically significant correlations of resistin were detected with respect to the initial proteinuria of a single case (r = 0.32, p = 0.04) and daily proteinuria (r = 0.39, p = 0.001). Dependence of resistin and parameters reflecting the renal function: urea, creatinine, GFR, determined initially and after 12 months, was not identified, nor was there a correlation with rates of decrease / increase of these parameters after 12 months. When performing logistic regression analysis, it was shown that, in nephritic and nephrotic variants, the level of resistin increases the probability of developing a number of morphological changes in the glomerulus exclusively in the renal glomeruli, in particular, the risk of detection of segmental sclerosis, predominantly mesangial deposition of immunoglobulin deposits, primarily IgA.
CONCLUSION. In the course of the study, there was no association of resistin with renal function factors (creatinine, urea, GFR), both initially and against a background of 12 months of observation and treatment. It has been shown that as the serum concentration of resistin increases, the level of proteinuria increases, and the likelihood of developing glomerular morphological changes, generally reflecting the severity of the glomerular lesion, increases.
THE AIM: retrospective and one-time evaluation of the main variants of renal pathology in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with an assessment of cardiovascular risk and basic biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction.
PATIENTS AND METHODS. The retrospective study included 780 patients with RA, 175 patients at one time, and 63 with nephrobiopsy. The frequency of various variants of renal damage was assessed on the background of RA, arterial hypertension, anemia. Serum concentration of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were determined. The comparison of the indices in the groups by the level of GFR (more than and less than 60 ml / min) was performed.
RESULTS. In patients with RA we find statistically significant differences in two groups by 10-year cardiovascular risk according to the SCORE scale was presented. Other statistically significant factors were age, the frequency of arterial hypertension, anemia, obesity, the activity of endothelial dysfunction biomarkers. Tubulointerstitial nephritis was recorded in 27 of 63 patients with nephrobiopsy performed.
CONCLUSION. Chronic kidney disease in patients with RA can be associated with cardiovascular factors – SCORE index, progressive endothelial dysfunction, age, arterial hypertension, anemia, obesity, but not with the pro-inflammatory activation.
THE AIM: to study the functional capacity of the kidneys in women with alimentary obesity under pre-eclampsia.
PATIENTS AND METHODS. The study included 145 pregnant women in a period of 37-40 weeks. The first group included 60 pregnant women with preeclampsia of moderate severity. In the second – 63 pregnant women with preeclampsia of moderate severity and alimentary obesity. Control group – 22 women with physiological pregnancy. All pregnant women have assessed the rate of glomerular filtration, β2-microglobulin in urine, studied the osmoregulating function of the kidneys, colloid-oncotic pressure, as well as the concentration of leptin.
RESULTS of the studies showed that 79.4% of women with preeclampsia of moderate severity had a violation of the functional state of the kidneys. In 86.7% of patients from this group, there were quite pronounced violations of colloid-oncotic homeostasis. In 93.7% of women with preeclampsia of moderate severity and obesity, violations of osmotic and metabolic functions of the kidneys were more pronounced than in the first group.
CONCLUSION. Combined disorders of colloid-oncotic pressure and the syndrome of “hypoperfusion” leading to the transformation of osmotic and metabolic functions of the kidneys are the cause of the renal dysfunction formation in women with preeclampsia and obesity, involving in the pathological process of adaptation and regulatory systems of pregnant women.
THE AIM: to investigate the possibility of the use of urine biomarkers NGAL (neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin) and KIM-1 (kidney injury molecule-1) for early detection of damage to proximal tubules (PT) and tubulointerstitium in nondiabetic hypertensive patients with CKD stage 2.
PATIENTS AND METHODS. The research involved 60 patients (16 men and 44 women, mean age 60,4±8,37 years) with primary and nephrogenic hypertension, which were divided into 3 groups: 1 gr. with GFR>85 ml/min/1,73 m2 ), 2 gr. with GFR 60-74 ml/min/1,73 m2 ), and 3 gr. with GFR<60 ml/min/1,73 m2 ), The control group consisted 15 normotensive individuals (6 men and 9 women, mean age 49,8±9,68 years) without overt signs of kidney and cardiovascular diseases. All patients carried out a comprehensive survey with determination the content of urine NGAL («Human NGAL ELISA kit») and KIM-1 («Human KIM-1 Immunoassay ELISA»).
RESULTS. Increased NGAL content In the urine of patients 2 and 3 gr. were identified respectively in 2,62 and 7,22 times compared with the control group. Augmentation the concentration of KIM-1 in the urine of the same patients groups was respectively 2,12 and 3,14 times. Similar results were obtained in a selected group (n = 30) of hypertensive patients with chronic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Urinary NGAL concentration in the group of patients with mild renal dysfunction (GFR 67,2±5,93 ml/min/1,73 m2 ) was higher than the comparison group data in 2,36 times, and in the patients with severe renal impairment (GFR 53,6±6,67 ml/min/1,73 m2 ) – to 9,09 times (p < 0,05). Similar data growth KIM-1 content in the urine of the patients with CHFpEF were respectively 1,84 and 6,87 times (p < 0,05).
CONCLUSION. Urinary NGAL increase by more than 2,5 times and increase urinary KIM-1 more than 2 times compared with normal values can be diagnostic marker of early damage of PT and tubulointerstitium in nondiabetic hypertensive patients with stage 2 CKD.
JOURNAL IN THE JOURNAL. ACTUAL PROBLEMS OF UROLOGY
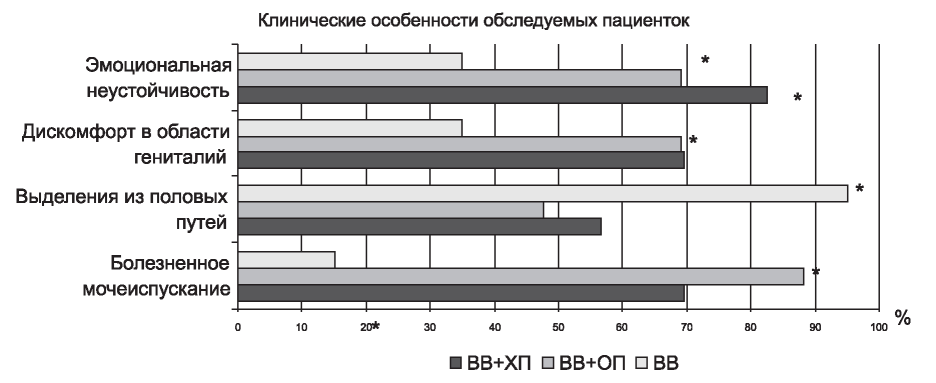
THE AIM: to study the characteristics of the vaginal flora and to evaluate the efficacy of bacteriophage in complex treatment of urogenital infections in girls.
PATIENTS AND METHODS. Prospective controlled randomized study was conducted in 88 girls aged 3-6 years with urogenital infections, of which 1 group (n=46) – vulvovaginitis (VV) against the background of exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis; group 2 (n=42) – VV on the background of acute pyelonephritis (AP); group 3 (n=40) – isolated VV. Depending on the correction method, all the patients were divided into receiving standard treatment and treatment with complex application of bacteriophages.
RESULTS. It was revealed that the duration, number of relapses VV and trips to the gynecologist after the standard treatment of VV in the examined groups was significantly higher compared with the complex treatment with the use of bacteriophages.
CONCLUSION. Anti-inflammatory therapy of VV, including the use of complex bacteriophages, improves the condition of the vaginal biotope, decreases microbial colonization, reduces the number of relapses explosive preschool girls suffering from acute and chronic pyelonephritis.
THE AIM: to evaluate the clinical significance of the use of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and its fractions and indexes for early detection of prostate cancer (PCA) in men with total PSA (tPSA) 2-10 ng/ml with a negative digital rectal examination (DRE).
MATERIALS AND METHODS. It were examined 904 men aged 45-80 years with tPSA 2-10 ng/ml (Hybritech calibration) and a negative result DRE. Morphologic study of 628 people were identified benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and 276 – PCA. All patients underwent ultrasound examination of the prostate, with determined total PSA (tPSA) concentration, its fractions and indexes.
RESULTS. In PCA, the relative concentrations in the serum free PSA was 19% lower and the absolute content [-2]proPSA at 42% higher, and the prostate health idex (PHI) – at 49% higher. At low values of tPSA for prostate cancer would not be diagnosed in 9%, and at normal values of – 28% of patients. The sensitivity of the method at tPSA of 4.0 to 10.0 ng/ml is 0,630 and specificity of 0,519. tPSA, %fPSA were negative, but [-2]proPSA, %[-2] proPSA and PHI is positively correlated with the Gleason sum. All indicators in stage 2 for PCA are significantly different from the values characteristic of stage 1 of the disease. Though, for commonly used metrics – tPSA, fPSA and %fPSA – differences did not exceed 22-27%. However, [-2] proPSA, %[-2]proPSA and PHY at stage 2a increased by 20-53%, and at stage 2b – by 55-77%.
CONCLUSION. The most informative indicators for early diagnosis of PCA was PHY, [-2]propsa. Determinatioms of PHY in the dynamics within the screening can substantially improve early diagnosis of PCA.
THE AIM: the comparative study of morphological changes in kidney tissue with mechanical ureteral obstruction in the experiment at the time of 7, 14, 21 days.
Matherials and methods. The study of the dynamics of the morphological changes in the kidney showed that in the first 7 days after obstruction, there are compensatory reactions from the tubular apparatus of the medulla of the kidneys and minimal development of interstitial fibrosis.
Results. In the subsequent terms (14-21 days), compensatory phenomena in the epithelial cells of the tubules are disrupted autoregulatory mechanisms of adaptation, which is manifested in the phenomena of protein, hydrops dystrophy, atrophy, cystic transformation of epithelial cells of the tubules of the cortex and medulla layers, and the appearance of large zones of interstitial fibrosis of the stroma.
CONCLUSION. Obtained data make it possible to consider that the optimal period for performing surgical interventions, with obstructive uropathy, is the first week from the beginning of the development of the pathological process since this will prevent further development of dystrophic and atrophic changes in the tubular apparatus and sclerosis of the renal tissue.
THE AIM of the study was to examine the mechanisms of development of gestational pyelonephritis and placental insufficiency in the conditions of the experiment.
MATERIAL AND METHODS. Biological modeling conducted on 40 pregnant female rats of Wistar Kyoto line weighing 250-300 gr. In the first block of the experiment [I group (n=10), group II (n=10), control] have made glucocorticoid dysregulation through the use of glucocorticoid drug “prednisolone” from 3rd to 11th day of gestation (by method of Yu.Yu.Chebotareva, V.G. Ovsyannikov et al.) followed by determination of morphological changes of the fetus (weight, length) and histological analysis of the kidneys and Feto-placental complex. In the second block of the experimental study [III (CC) group (n=10), group IV (n=10), control] on the same background with 1 unit of glucocorticoid drug studied the specific features of pregnancy, labor, the condition of newborn rats (height, weight, developmental abnormalities). Used in this experiment methods of anesthesia, the killing of rats corresponds to the principles of the Helsinki Declaration about the humane treatment of animals. The experiment was carried out, taking into account international standards and requirements for use in non-clinical studies quality animals in accordance with the Principles of good laboratory practice (national standard of Russian Federation GOST R 53434-2009, March 2010), which provides the conducting of all preclinical, extraclinical and expert researchers in accordance with international standards of GLP.
RESULTS. It is revealed that the experimental simulation of disorders of reproductive function in rats by hormonal balance violations forms gestational pyelonephritis and placental insufficiency, which is manifested by the increased number of aborts, intrauterine growth retardation of fetuses, decrease their weight.
CONCLUSION. In the present experimental study refined the role of glucocorticoid dysregulation in the development of gestational pyelonephritis, placental insufficiency.
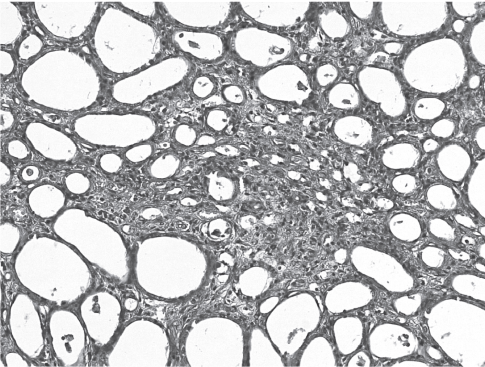
THE AIM was to study morphological changes in the contralateral kidney in the dynamics of obstructive uropathy development.
MATERIAL AND METHODS. Morphological examination of the contralateral kidney with obstructive uropathy on days 7, 14 and 21 revealed a number of characteristic structural changes in the tubular apparatus and interstitial substance.
RESULTS. During the first 7 days of obstruction development, dystrophic changes predominated due to disturbance of waterelectrolyte, protein metabolism (hyaline-droplet, hydrophilic dystrophy of the tubular apparatus), after 14-21 days changes occurred in the stroma of the renal tissue. It should be noted the emergence in these terms of the so-called mesh fibrosis, localized between individual tubular structures of the medulla of the kidney with following the development of neoangiogenesis in it.
Conclusion. The described morphofunctional patterns of changes in the contralateral kidney in experimental obstructive uropathy will give an idea of not only the severity of water-electrolyte disorders but also the timing of early development of fibrosis and neoangiogenesis of the renal parenchyma.
ANNIVERSARIES
ISSN 2541-9439 (Online)