LEADING ARTICLE
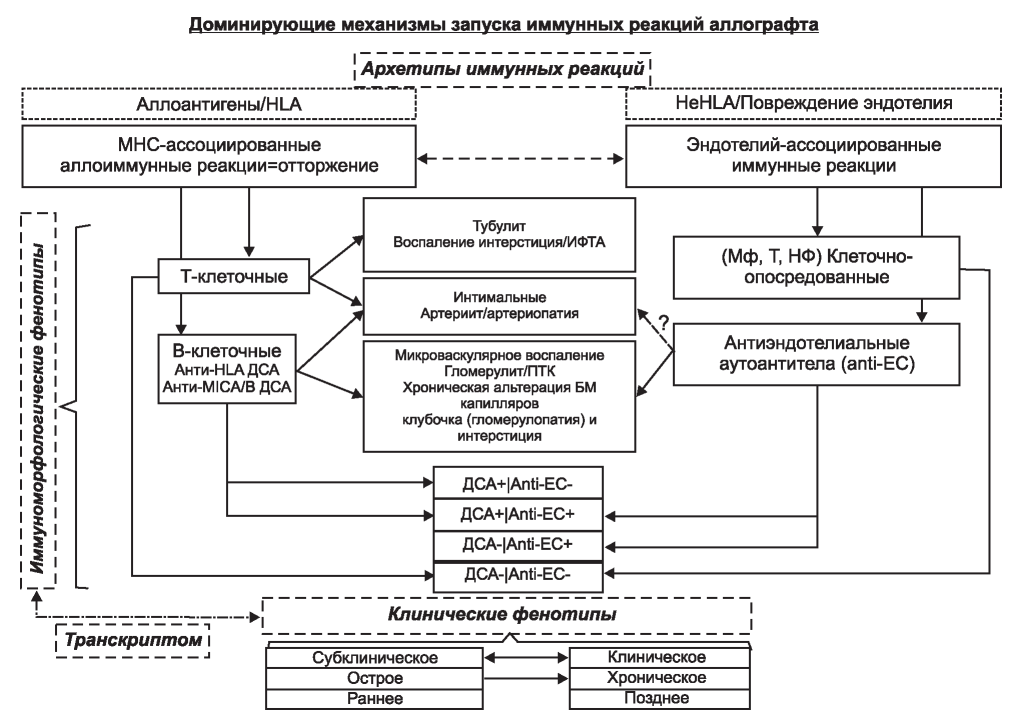
Long-term outcome of kidney transplantation is limited by the development of allograft rejection due to activation and realization of Tand B-cell immune response as well as the effects of other types of immune reactions mediated by various mechanisms. This article is dedicated to nowadays point of view upon the different immune and morphological phenotypes of kidney transplant injury. Main focus is made on the pathways of microvascular inflammation in the case of donor-specific antibodies absence as the unique self-sustained phenotype of the kidney allograft injury.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
New-onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation (NODAT) in kidney transplant recipients promote the development of complications and have a negative impact on kidney transplantation (KT) results.
Aim. Comparison of clinico-demographic characteristics and KT results in recipients with and without NODAT.
Patients and methods. Study included 439 patients 18+ years without pre-transplantation diabetes who underwent KT from the deceased donor in our center from 01.01.2007 to 31.12.2016. All patients after KT received calcineurin inhibitors and mycophenolate, 322 received tacrolimus (TAK), 117cyclosporin A (CsA). Seventeen recipients received immunosuppression without steroids.
Results. NODAT developed in 41 (9.3%) of 439 patients: 33 (10.2%) of 322 on TAK, and 8 of 117 (6.8%) on CsA, p=0.368. The groups with NODAT and without NODAT did not differ in gender, proportion of patients with polycystic kidney disease, modality and duration of dialysis, features of immunosuppression, although there was a tendency for older age and higher body mass index in patients with NODAT. In NODAT group there were significantly more patients with preexisting metabolic syndrome (31.7% versus 12.3%, p = 0.002), post-transplant surgical complications (21.9% vs. 8.5%, p= 0.012), fungal infections (14.6% vs 5.0%, p=0.026), cardiovascular complications (26.8% vs. 9.8%, p=0.003), patients who died with functioning graft (17.1% % vs. 5.5%, p = 0.0012). Recipients and transplants survival was significantly lower in NODAT group (p=0.008, p=0.022, resp.).
Conclusion. NODAT negatively affects the results of KT. Prevention, early detection and adequate treatment of NODAT can reduce the incidence of complications after KT and improve recipients and transplants survival.The Aim of the study was to assess the association of T-cell (CD3+), monocyte/macrophage (CD68+), B-cell (CD20+) infiltrates in glomeruli with long-term kidney allograft survival in patients with renal allograft (RA) glomerulitis.
Patients and methods. 97 RA recipients with biopsy-proven glomerulitis were enrolled in this retrospective study. 54,6% of patients were negative for donor-specific antibodies (DSA-) at the time of biopsy. DSA were detected in 25,8% of cases (DSA+). For 19,6% of patients DSA evaluation was unavailable at the time of biopsy. Morphological findings were assessed according to the Banff 2013 criteria. After immunohistochemical staining for CD68+, CD3+, CD20+ cells quantitative assay of positive cells in glomerular capillaries was performed. The Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards regression model were used to evaluate the relationship between intraglomerular CD3+, CD68+, CD20+ cells and risk of RA loss.
Results. CD68+ and CD3+ cells were found in glomeruli in RA glomerulitis more frequently than CD20+ cells. The level of intraglomerular CD68+ cells was higher in DSA+ group (p = 0,005), there was no difference in the level of CD3+ and CD20+ cells between DSA subgroups. Infiltration of CD68+ ≥ 8 cells per glomerulus was associated with a lower RA survival (p log-rank = 0,019) as well as infiltration of CD3+ ≥ 1 cell per glomerulus (p log-rank = 0,029). The number of glomerular CD68+ (1 cell per glomerulus) was independent predictor of RA loss in multivariate Cox regression model (p ≤ 0,003).
Conclusion. RA glomerulitis could be realized by different immunological pathways including monocytes/macrophages actions that requires further investigations. Immunomorphological evaluation of immune cells subpopulations, in particular CD68+ cells, could be crucial for the evaluation of long-term RA prognosis and appropriate therapeutic approach.
Introduction. Kidney transplant (KTx) with reduced functional reserve is more sensitive to the toxic effects of calcineurin inhibitors (CNI). Immunosuppressive (IST) approach included m-TOR inhibitors in case of KTx from the ECD lead to decreasing levels of cyclosporine (CsA) in the blood. Despite of presence international pilot studies we having not yet strong recommendation for real combination of CsA and Everolimus. In this article we presented 5-yeras results of the first Russian experience of systematic use Everolimus as basic IST in KTx from ECDs.
Patients and methods. The group of recipients (n=41) was formed during the operation; received a bilateral kidney transplants from the same ECDs. Comparison group (n=19) received standard IST consisting of CsA, MMF and steroids. Study group included 22 recipients who received an another kidney from the same ECD and IST, based on early (starting from the 90th day after transplantation) conversion from MMF to Everolimus-1.5mg/day (target concentration-3-6ng/mL). Simultaneously with the appointment Everolimus, dosing occurred immediately Neoral decrease by 50% and then, in accordance with the target concentration (C0-30-50ng/ml). Implementing a program of gradual minimization of the dose steroids in patients of the study group.
Results. Both groups were comparable in terms of level of serum creatinine and glomerular filtration rate of up to 3 months after transplantation. As a result of the introduction of a new scheme of ICN in the study group, for the 60-month observation GFR study group was 46±15 ml/min/1.73m2, the control is reduced to 28±7 ml/min/1.73m2;P<0.05.
Conclusion. Early administration of Everolimus is strongly recommended in all cases of the use of grafts for KTx obtained from the ECDs. This approach helps to minimize of nephrotoxity of CNT, provides the prevention of chronical transplant nephropathy, the stable renal function, and contributes to the survival and renal transplant recipients.
Background: The progression of diabetic nephropathy (DN) often accompanies by a combination with non-diabetic glomerulopathies (NDGP), which can significantly affect the prognosis and treatment of patients. However, the information about such influences, in particular, on the severity of tubulointerstitial fibrosis, one of the main pathomorphological prognostic criteria, on the renal parenchyma is not enough. AIM: To investigate the significance of NDGP for fibrotic processes kidney parenchyma in patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN).
Patients (materials) and methods: Single-center retrospective analysis based on medical records of 51 patients (32 men, mean age: 49±13 years) with DN who underwent renal biopsy between 2002 and 2016. All patients were diagnosed as cases of DN -gr.№1, those were divided on “pure” DN-gr.№2 and DN-gr.№3 with NDGP.
Results: Out of the 51 DN gr. №1 patients, 30 (60. %) had gr. № 2, 21 (40. %) had gr. №3. IgA nephropathy (IgAN)-20 % was the most common GN followed by focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)-35%, and HCV –associated GN was the most common secondary GN. Patients with “pure” DN had lower estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR) and higher value of systolic blood pressure (SBP), glomerulosclerosis ( GS), peritubular capillarirtis ( PTC) and myofibroblasts quantity ( SMApositive cells). No significant between-group differences were observed with respect to majority of laboratory and morphological features. The activity of myofibroblasts positively correlated with tubular atrophy, focal sclerosis, the stage of diabetes and GS in gr. №2 in comparison with gr. № 3.
Conclusions: The fibrosis of tubulointerstitium in the kidney of patients with DN accoppanied the pathomorphological markers such as SMA and PTC . There wasn’t significant evidences about the differences of fibrotic processes in the renal parenchyma in patients with and without NDHD.
The quantification of specific urinary proteins in high-grade proteinuria can be of importance for the evaluation of mophrological lesions, response to therapy and prognosis.
The aim of our study was to analyze whether the urinary excretion of high and low molecular proteins associated with the degree of glomerular, tubulointerstitial and vascular fibrosis.
Patients and methods. The study included 97 patients with biopsy proven primary immune glomerulopathies: membranous nephropathy (n =22), minimal change disease (n=13), focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (n =30), IgA nephropathy (n=32). Measurements of total protein, immunoglobulin G (IgG), transferrin (Trf), α1-microglobulin (α1-МG), β2-microglobulin (β2-MG) were performed by nephelometric method in morning urine samples. The results were standardized for urine creatinine (Cr) concentration.
Results. There were a correlation between proteinuria and specific proteins: β2-MG (r=0.24, р=0.025), α1-МG (r=0.38, р<0.001), Trf (r=0.78, р<0.001), IgG (r=0.67, р<0.001), as well as the positive correlation between high and low molecular proteins. Low molecular proteins (β2-МG, α1-МG) correlated with global glomerular sclerosis (r=0.28, р=0.010 and r=0.21, р=0.049 respectively) while levels of proteinuria and high molecular weight proteins did not. Urinary excretion β2-microglobulin was also significantly higher in patients with moderate-to-severe tubulointerstitial and vascular fibrotic lesions.
Conclusion. β2-microglobulin was suggested to be candidate integrative biomarker of renal fibrosis in primary glomerulopathies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION
The aim. To assess the effect of enrichment of calcium and magnesium in drinking water on the level of arterial pressure (BP), myocardial remodeling processes, and autorhythmic contractile activity of the portal vein (PV) of spontaneously hypertensive SHR rats and control WKY rats.
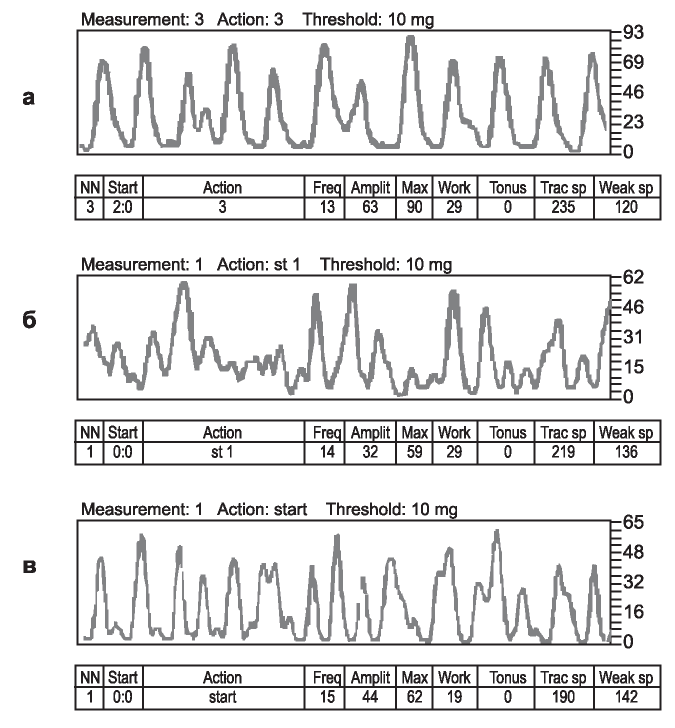
Material and methods. One group of SHR rats received drinking water enriched with calcium (120 mg/L) and magnesium (45 mg/L) from a 6-week-old age within 2 months. Two other groups of SHR and WKY rats received St. Petersburg tap water with a low content of Са2+ (8 mg/L) and Mg2+ (3 mg/L). All groups received a standard diet. At the end of the observation period, rats were assessed with blood pressure, myocardial mass index, urea level (UR), total cholesterol (Chol), total calcium (totalCa) and albumin (Alb) in blood. A contractile activity of PV was investigated by the method of myography (in vitro). The total and maximal amplitude and frequency of contractions of PV, as well as the work done by PV was determined.
Results. In SHR rats, the enrichment of drinking water of Са2+ and Mg2+, prevented the progressive rise BP to the level characteristic of the SHR, resulting in its stabilization at 18% lower than in the SHR of the mineral deficient group. Theincreaseinthecontent of Са2+ and Mg2+ in drinking water did not affect the degree of myocardial hypertrophy, as well as on the level of UR, totalCa and Alb of blood, but led to a decrease in the level of total cholesterol compared to animals that received low-mineralized water. The options of the autorhythmic contractile activity depended on the mineralization of drinking water. The addition of Са2+ and Mg2+ to the drinking water of SHR rats resulted in a decrease in both the amplitude of contractions of PV and the work performed by PV as compared with rats of mineral deficient groups.
Conclusion. The researches have shown the important role of mineral composition of drinking water in processes of regulation of a level of arterial pressure. In spontaneously hypertensive SHR rats, the antihypertensive effect of drinking water enrichment with Са2+ and Mg2+ has been revealed. The increase in the intake of exogenous calcium and magnesium with water modifies the autorhythmic contractile activity of the portal vein of spontaneously hypertensive SHR rats, normalizing it to a level characteristic of normotensive WKY rats.
Objective: to compare the indicators of iron metabolism, the level of hypoxia induced factor (HIF-1α) and erythropoietin (EPO) in children with anemia in CKD Stage 1-5.
Patients and methods: three groups of patients: I – 32 children under dialysis with CKD Stage 1-5 without therapy, II – 18 children up to dialysis CKD Stage 2-5 receiving treatment with iron and ESP, group III – 30 dialysis patients with CKD Stage 3-5 receiving treatment with iron and ESP. Serum levels of EPO and HIF-1α was determined by solid-phase chemiluminescent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method (sandwich) using a test system Biomerica EPO ELISA kit to determine the level of HIF-1α, Cloud-Clone Corp.
Results: In the I group, a statistically significant increase in the level of HIF-1α (0,089 ± 0,011ng / ml) was found compared with the mean normal (0,043 ng / ml) (p = 0.0001). In the II group, an increased level of EPO (63,01 ± 14,84 MIU / ml) was found in comparison with normal (17,56 MIU / ml) (p = 0,0088), an increase in HIF-1α (0,138 ± 0,025 ng / ml) compared with normal (0,043 ng / ml) (p = 0.005). A comparative study of EPO and HIF-1α in children with CKD showed a statistically significant increase in EPO and HIF-1α in the II group before dialysis (on therapy) compared to group I before dialysis (without therapy). A correlation between GFR and HIF-1α was established in group II patients.
Conclusion: A direct correlation between the level of GFR and HIF-1α in the blood was revealed in patients of group II with CKD Stage 2-5 before dialysis, receiving preparations of erythropoietin and iron. In the I group, before dialysis (without therapy) and III group of dialysis patients receiving ESP and iron, the binding strength of GFR and HIF-1α is not significant.
PRACTICAL NOTES
AL-amyloidosis is a disease associated with the clonal plasma cell proliferation and aberrant immunoglobulin light chain secretion. Deposition of insoluble polymers composed of monoclonal light chain lead to disruption of tissue architecture and organ dysfunction. Infiltrative amyloidogenesis often results in restrictive cardiomyopathy, leading to progressive heart failure, and kidney involvement with nephrotic proteinuria and dysfunction. Diagnostic is based on findings of tissue amyloid deposition and confirmation of monoclonal light chain nature. Here we reported course, diagnostic and successful treatment of primary AL-amyloidosis case with unusual disease presentation with lungs and pleura involvement, resulting further in heart and kidneys injuries.
ITG (immunotactoid glomerulopathy) cases in patients with multiple myeloma (MM) are extremely rare. We present a clinical case of a patient with MM Gκ who developed nephrotic syndrome, macrohematuria and acute kidney injury. Kidney biopsy revealed microtubules in glomerular basement membrane 19 nm in diameter, organized in bundles. The patient was treated with bortezomib, cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone (BorCyDex) and achived complete remission after 6 cycles of therapy with a complete renal function recovery. Repeated renal biopsy has revealed a complete resorption of the deposits. Later the patient has received autologous hematopoietic stem cells transplantation (auto-HSCT). After 2 years, an immunochemical relapse of MM has developed. Nephropathy signs have appeared 4 years after auto-HSCT, ITG was diagnosed again on kidney biopsy during MM relapse with microtubules 11-12 nm in diameter. A special characteristic of our case was excessive glomerular infiltration by the lymphoid cells with capillary lumen obstruction. We consider the build-up of lymphoid cells in the glomerulal capillaries lumen as a special variant of renal tumor lesion in MM. Lymphoid cells had signs of plasmatization. Bundles of microtubules, similar to the deposits in kidneys, were revealed in some of lymphoid cells. The data obtained confirm that microtubules are formed in plasma cells that situated in the lumen of glomerular capillary vessels and later migrate into renal structures.
ANNIVERSARIES
In 2017, 20 years have passed since the launch of the Dialysis Department of St. Petersburg City Hospital No. 15 – one of the largest dialysis centers in St. Petersburg.
INDEXES
ISSN 2541-9439 (Online)