LEADING ARTICLE
Currently, fundamental nephrology includes many sections of related sciences, giving a new way to understanding the mechanisms of kidney functioning at the molecular level. The authors of the article emphasize that the basis of kidney function comprises molecular systems, including a variety of receptors, cotransporters, pumps and ion channels, which ultimately provide the body's homeostasis. Fundamental nephrology, which is a synthesis of physiology and molecular OMIX-research, allows the doctor to more deeply delve into the essence of pathological processes, to diagnose kidney disease at the preclinical level. The close relationship between fundamental and clinical nephrology provides not only the translation of scientific advances into practice, but also contributes to the personification of therapy.
REVIEWS AND LECTURES
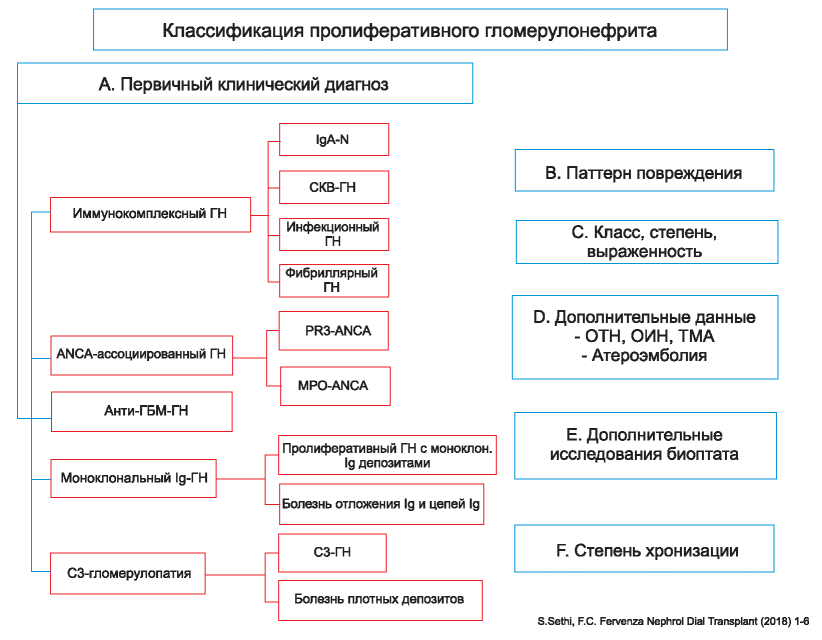
A kidney biopsy is done to determine the etiology of the glomerulonephritis (GN) and the severity of the lesion, to identify whether other lesions, related to or not related to the GN, are present on the kidney biopsy and finally to ascertain the extent of chronicity of the GN. The etiology of GN is based on the classification of GN into five groups: immune complex-mediated GN, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated GN, anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) GN, monoclonal immunoglobulin-mediated GN and C3 glomerulopathy. Immune complex GN includes multiple specific diseases such as lupus nephritis, IgA nephropathy, infection-related GN and fibrillary GN. ANCA GN, anti-GBM GN and C3 glomerulopathy are specific diseases in themselves, while monoclonal Ig GN includes proliferative GN with monoclonal Ig deposits and monoclonal Ig deposition disease. Thus identification of the class of GN and within it the specific disease determines the etiology of GN. Ancillary studies may be required to confirm the etiology of GN. The severity of the GN is revealed by the pattern of injury, such as crescentic, necrotizing, diffuse proliferative, exudative, membranoproliferative, mesangial proliferative or a sclerosing GN. Secondary diagnosis either related or unrelated to the GN, such as diabetic glomerulosclerosis, acute tubular necrosis or thrombotic microangiopathy, may also be present. The secondary diagnosis may sometimes be the reason for the kidney biopsy. The chronicity of GN is determined by evaluating the extent of glomerulosclerosis, tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis and vascular sclerosis present on the biopsy. This review summarizes the approach to standardizing a kidney biopsy report that includes these components in a logical and sequential manner.
Translation by D.A. Mayer, T.O. Muzhetckaya, A.O. Mukhametdinova, M.S. Khrabrova.
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) is one of the common chronic viral infections. Current advances in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C have allowed WHO to develop a Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis for 2016-2021 with the purpose of its elimination by 2030. Antiviral drugs of new generations have therapeutic efficacy of more than 98% and wide indications for use. At the same time, there are special groups of patients in whom the choice of antiviral therapy regimen is limited and its effectiveness differs from the general population of patients with chronic hepatitis C. This review provides data on the epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations of CHC, and current approaches to the treatment of the disease. Particular attention is paid to patients with extrahepatic manifestations of chronic HCV infection.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
Background. Chronic kidney disease affects almost all organ systems. Respiratory lesions in these patients are often underestimated in clinical practice. THE AIM. Diagnosis and clinical evaluation of the respiratory system in patients with high-flux hemodialysis to optimize the treatment of patients with chronic kidney disease.
Patients and methods. There were 60 patients examined. Two groups were considered: the main group - patients with chronic glomerulonephritis (in 17 patients, the diagnosis was confirmed morphologically) with stage 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD), receiving hemodialysis therapy (n = 30), and the comparison group - patients not receiving dialysis (n = 30). Experience of smoking, results of clinical, biochemical blood tests and respiratory tests - vital capacity (VC), forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), FEV1/FVC and maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV) were studied in all patients.
Results. The mean body mass index (BMI) in the main group of patients was 28 ± 6 kg/m2, and in the comparison group, the average BMI was 24 ± 3 kg/m2. BMI in groups as a whole was not significantly different (p = 0.40). In the general group, 29% had an increased level of triglycerides. No significant differences were found between the results of the respiratory tests of the two group (p>0.05).
Conclusion. FVC decreases in women receiving hemodialysis treatment; there is a decrease in FEV1/FVC in proportion to the duration of hemodialysis treatment in men. Increasing levels of C-reactive protein in patients on hemodialysis accompanied by a decrease in FVC; an increase in triglyceride levels accompanied by a decrease in the FEV1/FVC index.
Background. In experimental and clinical medicine, new data and ideas on the role of so-called “ectopic” chemosensory receptors expressed outside their canonical localizations have appeared. As for receptors for umami-substances, to date, certain data have been obtained on both receptors in the tongue and extraoral in the kidneys (monosodium glutamate as the best-known ligand). At the same time, the functions of these receptors are still not completely understood.
The aim of the study was to assess the sensitivity of glutamate receptors to monosodium glutamate in bronchial asthma using the threshold measurement and to compare it with the glomerular filtration rate in the same patients.
Patients and methods. 54 practically healthy individuals, 55 patients with bronchial asthma were examined. To assess the taste sensitivity to monosodium glutamate, solutions of monosodium glutamate were prepared at concentrations of 0.067; 0.1; 0.2; 0.3; 0.4; 0.5%. The concentration at which the taste of meat broth was felt was considered the threshold concentration of the sensation of umami taste. Glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) by CKD-EPI was calculated.
Results. In patients with bronchial asthma, a significant direct correlation was found between the threshold measurement and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (high sensitivity to sodium glutamate correlates with a reduced glomerular filtration rate). Sensitivity to sodium glutamate is also directly related to indicators reflecting inflammation (the content of neutrophils, monocytes in peripheral blood, C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
Conclusion. In bronchial asthma, the use of gustometry measurement has revealed the phenomenon of high sensitivity to monosodium glutamate, which correlates with a reduced glomerular filtration rate and inflammation ndices. It is suggested that the revealed features of glutamatergic signaling may serve as a common pathogenetic mechanism both in bronchial asthma and chronic kidney disease.
Background. To assess the effect of duration of hemodialysis therapy on the body composition of patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5. To study the cumulative survival of patients receiving chronic hemodialysis therapy, depending on changes in their body composition and nutritional status.
Patients and methods. 84 patients with terminal kidney disease from one hemodialysis center were observed for two years. Diamant-AIST device was used for the evaluation of the compartments' volumes and nutritional status.
Results. Negative correlations between the time on the hemodialysis treatment and studied bioelectrical impedance analysis parameters were observed: correlation with total fluid volume (r=-0,6, p<0,05), fat free mass (r=-0,558, p<0,05), free water volume (r=-0,588, p<0,05), fat mass (r=-0,458, p<0,05), lean body mass (r=-0,564, p<0,05), active cell mass (r=-0,5, p<0,05). There was a statistically significant difference between the cumulative survival with regard to mortality from all causes and cardiovascular events of the patients with high and low values of the fat body mass.
Conclusions. Our study showed that change in the compartment's volumes is associated with the length of hemodialysis treatment. There is a statistically significant difference in survival of patients with low and high free fat mass.
The aim: to clarify the safe range of the values of the corrected QT interval and to identify risk factors that contribute to its increase in patients with end-stage renal disease who receive treatment with programmed hemodialysis (HD).
Patients and methods. 70 patients (26 men and 44 women) with end-stage renal disease receiving HD were observed for 5 years. The average age was 58.5 ± 14.7 years. A traditional clinical and laboratory examination, echocardiography was performed in all patients. The value of the QT interval corrected for the frequency of ventricular contractions was calculated using the Framingham formula. The patients were clinically stable, there were no violations of heart rhythm and conduction requiring medical correction.
Results. During 5 years of observation, 23 patients died. Given the different number of men and women among the surveyed, mortality rates were calculated separately for each of the gender groups. For men, mortality was 27% or 6.7 per 100 patient-years (6.7 per 100 people per year). For women, respectively, 36.4% or 8.5 per 100 patient-years (8.5 per 100 people per year). The chance of sudden cardiac death for men was 0.37, for women - 0.57. Thus, the risk of sudden cardiac death in women was 1.5 times higher than in men. The guidelines for the QT interval are proposed for the general population. We calculated the prognostic value of the QT interval in relation to sudden cardiac death in our patients was 440 msec or more; the area under the ROC curve is 0.978 (95% CI 0.911-0.998), p = 0.0001. Sensitivity 95.6%, specificity 100%. A number of identifiable indicators during the five-year observation period has changed (delta). There were identified correlations between the value of QT and the delta of body mass index Rs = -0.458 p = 0.002; delta of hemoglobin Rs = -0,338 p = 0.025; delta width of the distribution of platelets by volume Rs = 0.377 p = 0.011.
Conclusion. The data of our study allow us to offer for practical application a dynamics study of the PQ interval in comparison with the dynamics of body mass index, hemoglobin level and the width of the distribution of platelets by volume. This approach seems to us very important primarily in clinically stable patients with the PQ ≥ 440 msec interval corrected for the frequency of ventricular contractions.
The aim: to identify the correlations between cognitive dysfunctions and biochemical factors of blood - S100B protein and neuron-specific enolase - in young and middle-aged patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Stages 1-3.
Patients and methods. 108 young and middle-aged patients with chronic kidney disease Stages 1-3 were examined. 70 patients (64.8%) were diagnosed with chronic kidney disease Stage 1, 18 patients (16.6%) had CKD Stage 2, and 20 patients (18.5%) had CKD Stage 3 (A+B). Cognitive dysfunctions were assessed with MMSE survey and software package Status PF.
Results. The patients with CKD Stages 2-3 showed a higher degree of cognitive dysfunctions than those with CKD Stage 1. Statistically significant differences in the average exposure in simple visual-motor response (p=0.008) and minimal and average exposures in complex visual-motor response (р=0,004; р=0,0001) between these two groups of patients were discovered. A statistically significant negative correlation between the level of S100B protein and the glomerular filtration rate was found (Rs=-0,37; p=0,001). Positive correlations were discovered between the minimal exposure in complex visual-motor response and the level of cystatin C, and the average exposure in complex visual-motor response and the level of cystatin C (Rs=0,50, p=0,001; Rs=0,37, p=0,01), while negative correlations were found between the number of errors in complex visual-motor response and the level of cystatin C (Rs=-0,33, p=0,02). Positive correlation was discovered between the level of S100B protein and the minimal and average exposures in complex visual-motor response (Rs=0,29, p=0,001; Rs=0,39, p=0,001). A weak positive correlation was found between the level of S100B protein and the number of delays in reactions to the moving object (Rs=0,23; p=0,04). Statistically significant negative correlations were discovered between S100B protein and the total anticipation time and the number of accurate reactions in tests with moving objects (Rs=-0,39, p=0,001; Rs=-0,31, p=0,001). No correlations between neuron-specific enolase and neurodynamic indicators were discovered.
Conclusion. Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Stages 1-3 demonstrated minor cognitive dysfunctions associated with the glomerular filtration rate, cystatin C level, and S100B protein level.
The aim: to compare the quality of life (QOL) in hemodialysis (HD) patients with diabetes and without it and to evaluate the impact of diabetes on QOL variables.
Patients and methods. 192 prevalent HD patients completed the Kidney Disease Quality of Life Short Form (KDQOL-SF™) questionnaire. Of these, 23 patients had diabetes.
Results. Compared with non-diabetic HD patients, HD patients with diabetes scored lower on physical component of QOL: the Physical functioning scale - 30.0 (10.0-45.0) vs 65.0 (40.0-80.0) (Me[IQR]), p<0.0001; Bodily pain - 45.0 (32.5-67.5) vs 57.5 (45.0-90.0), p=0.046; Physical Component Summary (PCS) - 25.4 (20.5-35.3) vs 36.6 (29.8-44.5), p<0.0001. In the presence of diabetes, the Odds Ratio (95% CI) of the Role Physical scale score being below 50 were 6.7 (1.5-29.6) times higher than in the absence of diabetes. The Vitality scale score was also lower in diabetic HD patients: 40.0 (25.0-45.0) vs 45.0 (35.0-60.0), p=0.006. Regarding the dialysis-specific scales, diabetic patients had poorer scores than non-diabetics on Symptoms/problems - 64.6 (58.3-70.8) vs 75.0 (62.5-85.4), p=0.012 and Sleep - 47.5 (35.0-62.5) vs 57.5 (45.0-72.5), p=0.012. In the presence of diabetes, the Odds Ratio (95% CI) of the Work status scale score being below 50 were 7.8 (1.8-34.3) times higher than in the absence of diabetes.
Conclusion. Diabetic HD patients scored significantly lower than non-diabetic on the scales of self-reported physical health, Vitality, Symptoms/problems, Sleep and Work status.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION
The aim: to evaluate changes in endothelium-dependent regulation of the tone of blood vessels (aorta and superior mesenteric artery) in rats 4 months after the removal of 5/6 renal tissue.
Material and methods. An experimental CKD model was created by resection of 5/6 mass of renal tissue. The experimental group included animals (n = 12), subjected to nephrectomy (NE). The control group consisted of sham-operated (SO) rats (n = 10). Researches of vascular reactivity were performed on ring segments 2 mm long, which were excised from the aorta and superior mesenteric artery (SMA). A total of 23 segments of the aorta and 17 segments of SMA from rats after NE and 18 segments of the aorta and 15 segments of SMA from control animals were prepared. To measure the strength of contractions of the drugs, a FORT-10 sensor (WPI, USA) was used. The effects of acetylcholine (Ach, 1 x10-6 M) on blood vessels, previously exposed to phenylephrine (1 x10-5 M), and the response of vessels to Ach under conditions of prior exposure to TEA (1 x 10-3 mol / l) and L-NAME (1 x10-4 mol / l) were evaluated.
Results. NE for a period of 4 months led to arterial hypertension - BP in the NE group of rats was higher (165, 0 ± 9.8 mm Hg) compared with SO (127.2 ± 9.7 mm Hg, р<0,001), and to myocardial remodeling (LVMI in NE rat was 2.72 ± 0.11 mg / g compared to 2.35 ± 0.09 mg / in the SO group, р<0,001 ). NE led to a decrease in dilatation of aortic and BWA fragments on the ACh compared with LO animals. Under the conditions of NO blocking, the NO synthase inhibitor — L-NAME — also had a lower response to ACh in rats with NE. The preliminary blockade of the Ca2 + -activated K + channels of high conductivity with the introduction of TEA resulted in a decrease in vasodilation caused by ACh in NE rat compared with the SO group.
Conclusion. Resection of 5/6 of the kidney tissue mass in rats causes a decrease in vascular reactivity on the ACh. Endothelial dysfunction of rats after NE is associated with impairment of both NO-related and hyperpolarization-dependent endothelial cells in pathways of the vascular tone regulation.
PROGRAM ON CONTINUOUS POSTGRADUATE EDUCATION ON NEPHROLOGY
The review is devoted to the causes and mechanisms of proteinuria in various diseases associated with the development of the nephrotic syndrome. The contribution of damage to the main components of the glomerular filtration barrier, including the endothelium of glomerular capillaries, glomerular basement membrane, and podocytes, was analyzed. It is shown that the induction of proteinuria may be a consequence of disorders of the structure and function of each of these layers of the filter, as well as its combined damage. Special attention is given to the role of the glycocalyx and its components as well as reactive oxygen species and endothelial growth factor in the pathogenesis of disorders of the selective permeability of the capillary endothelium of the glomeruli in minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, pre-eclampsia, diabetogenic nephropathy. The significance of such genetic disorders of the glomerular membrane as Pearson and Alport syndromes is discussed. Gene mutations causing disorders of the structure and functioning of the main proteins of the actinic cytoskeleton of podocytes are considered separately.
Acute kidney injury (AKI), in contrast to acute renal failure, is a broader concept. Even minor changes in the excretory function of the kidneys have a significant impact on the work of the whole organism. The occurrence of AKI increases the risk of death, the length of hospitalization and the cost of treating any pathology. The purpose of this literature review is to analyze the possibilities of using a number of markers in the early diagnosis of various types of AKI in pediatrics. The review includes the most studied and applicable markers in pediatric practice - interleukin-18, Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL), kidney damage molecule-1 (KIM-1), cystatin C.
In 2000, the publishing house "Spetslit" published the monograph by of A.I. Nevorotin "Matrix phraseological collection: a manual for writing a scientific article in English". Despite the relatively large circulation (2000 copies), to present time date, this work has disappeared from sale and has not been reprinted. Thereby fore, it became necessary to publish the main provisions of the manuscript again. Moreover, in cut his case, a number of author's comments, notes and updates will be added in the present edition made. The Matrix phraseological collection is a kind of catalog of text samples. The samples were from articles selected from the leading English-language scientific journals and were systematized in such a way that when writing an article in English, Russian researchers are able easy to find examples suitable for his/her own work. Furthermore, the selected samples can be transformed accordingly saving the semantic and syntactic relations between the elements and, finally, be inserted into the text.
ISSN 2541-9439 (Online)